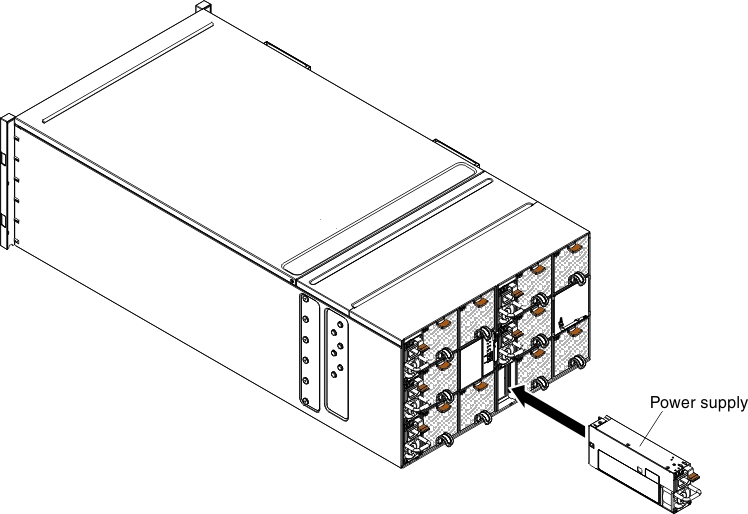
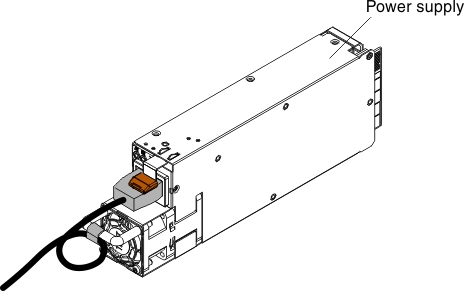
Use these instructions to install an AC power supply in the NeXtScale n1200 Enclosure. You can install an AC power supply while the NeXtScale n1200 Enclosure is powered on.
- Use only power supplies of the same power rating or wattage in each chassis.
- Make sure the input power is phase-to-phase, or, phase-to-neutral, 100 to 127 volt AC nominal, 50/60 Hz for low-line; or 200 to 240 volt AC nominal, 50/60 Hz for high-line power supplies.
- For 900-watt power supplies, if operating at low-line Vin (AC 100V - 127V), the power output can only be up to 600-watt. Up to 900-watt if operating at high-line Vin (AC 200V - 240V).
- You can only use 1300-watt power supplies with high-line Vin (AC 200V - 240V).
- Make sure that the power cord is not connected to the power supply when you install the power supply in the chassis.
- Do not remove the velcro strap from the rear of the power supply.
The following tables provide an indication of the quantity of nodes that can be installed in a chassis for specific processor types assuming nodes have all DIMM slots, PCIe slots, and hard disk drives populated. The tables are based on 900-watt or 1300-watt power supplies and the indicated power settings. However, when building a NeXtScale n1200 Enclosure solution, you are required to validate the power requirements for your configuration using the latest version of the Power Configurator to ensure that the number of power supplies selected are adequate for supporting your chassis configuration. Failure to validate the configuration with the Power Configurator tool could result in system errors, failure to power on, or microprocessor throttling, and limiting system's ability to leverage all of the microprocessor performance. The Power Configurator tool can be found at Lenovo Power Configurator download site.
| Microprocessor SKU (W) | # of micro- processor(s) |
Non-redundant or N+1 with OVS1, N=5 | N+1 redundant, N=5 | N+N redundant, N=3 | N+N redundant with OVS1, N=3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 2 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 12 | |
| 60 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 2 | 12 | 12 | 10 | 12 | |
| 70 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 2 | 12 | 12 | 8 | 11 | |
| 80 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 12 |
| 2 | 12 | 12 | 8 | 9 | |
| 95 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 10 | 12 |
| 2 | 12 | 12 | 6 | 10 | |
| 115 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 8 | 10 |
| 2 | 12 | 10 | 5 | 8 | |
| 130 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 7 | 9 |
| 2 | 10 | 8 | 4 | 7 |
| Microprocessor SKU (W) | # of micro- processor(s) |
Non-redundant or N+1 with OVS1, N=5 | N+1 redundant, N=5 | N+N redundant, N=3 | N+N redundant with OVS1, N=3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 9 | 11 |
| 2 | 12 | 12 | 6 | 10 | |
| 60 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 7 | 9 |
| 2 | 12 | 9 | 5 | 7 | |
| 70 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 7 | 9 |
| 2 | 12 | 9 | 5 | 7 | |
| 80 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 6 | 8 |
| 2 | 10 | 9 | 5 | 7 | |
| 95 | 1 | 12 | 11 | 6 | 7 |
| 2 | 9 | 7 | 4 | 6 | |
| 115 | 1 | 11 | 9 | 5 | 6 |
| 2 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 5 | |
| 130 | 1 | 9 | 8 | 4 | 5 |
| 2 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 4 |
| Microprocessor SKU (W) | # of micro- processor(s) |
Non-redundant or N+1 with OVS1, N=5 | N+1 redundant, N=5 | N+N redundant, N=3 | N+N redundant with OVS1, N=3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 2 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | |
| 60 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 2 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | |
| 70 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 2 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | |
| 80 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 2 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | |
| 95 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 2 | 12 | 12 | 10 | 12 | |
| 115 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 2 | 12 | 12 | 8 | 12 | |
| 130 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 2 | 12 | 12 | 7 | 11 |
| Microprocessor SKU (W) | # of micro- processor(s) |
Non-redundant or N+1 with OVS1, N=5 | N+1 redundant, N=5 | N+N redundant, N=3 | N+N redundant with OVS1, N=3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| 60 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| 70 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| 80 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| 95 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 5 + 1 microprocessor node | 6 | |
| 115 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 | |
| 130 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 5 + 1 microprocessor node | 6 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 4 + 1 microprocessor node | 5 + 1 microprocessor node |
| Microprocessor SKU (W) | # of micro- processor(s) |
Non-redundant or N+1 with OVS1, N=5 | N+1 redundant, N=5 | N+N redundant, N=3 | N+N redundant with OVS1, N=3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 5 + 1 microprocessor node | 6 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 | |
| 60 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 4 + 1 microprocessor node | 5 + 1 microprocessor node | |
| 70 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 4 + 1 microprocessor node | 5 + 1 microprocessor node | |
| 80 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 4 + 1 microprocessor node | 5 + 1 microprocessor node | |
| 95 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 4 + 2 microprocessor node | 6 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 5 | |
| 115 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 4 + 1 microprocessor node | 5 + 1 microprocessor node |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 3 + 1 microprocessor node | 4 + 1 microprocessor node | |
| 130 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 4 + 1 microprocessor node | 5 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 3 + 1 microprocessor node | 4 + 1 microprocessor node |
| Microprocessor SKU (W) | # of micro- processor(s) |
Non-redundant or N+1 with OVS1, N=5 | N+1 redundant, N=5 | N+N redundant, N=3 | N+N redundant with OVS1, N=3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 5 + 1 microprocessor node | 6 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 4 + 1 microprocessor node | 6 | |
| 60 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 4 + 1 microprocessor node | 5 + 1 microprocessor node | |
| 70 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 4 + 1 microprocessor node | 5 + 1 microprocessor node | |
| 80 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 4 + 1 microprocessor node | 5 + 1 microprocessor node | |
| 95 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 4 + 2 microprocessor node | 5 + 1 microprocessor node |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 5 | |
| 115 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 4 + 1 microprocessor node | 5 + 1 microprocessor node |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 3 + 1 microprocessor node | 4 + 1 microprocessor node | |
| 130 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 5 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 3 + 1 microprocessor node | 4 |
| Microprocessor SKU (W) | # of micro- processor(s) |
Non-redundant or N+1 with OVS1, N=5 | N+1 redundant, N=5 | N+N redundant, N=3 | N+N redundant with OVS1, N=3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 4 + 2 microprocessor node | 5 + 1 microprocessor node |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 5 | |
| 60 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 5 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 3 + 2 microprocessor node | 4 + 2 microprocessor node | |
| 70 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 5 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 3 + 2 microprocessor node | 4 + 2 microprocessor node | |
| 80 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 5 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 3 + 2 microprocessor node | 4 + 2 microprocessor node | |
| 95 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 4 + 2 microprocessor node |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 3 + 1 microprocessor node | 4 + 1 microprocessor node | |
| 115 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 3 + 2 microprocessor node | 4 + 2 microprocessor node |
| 2 | 6 | 5 + 1 microprocessor node | 3 | 3 + 2 microprocessor node | |
| 130 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 3 + 2 microprocessor node | 4 + 1 microprocessor node |
| 2 | 6 | 5 + 1 microprocessor node | 3 | 3 + 2 microprocessor node |
1300-watt and 1500-watt power supply supportability
The following table provides the 1300-watt and 1500-watt power supply supportability to have better performance and power efficiency.
| Quantity of 1300-watt power supplies | FPC power bank | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-redundant | N+1 redundant | N+N redundant | |
| 2 | Support | Non-support | |
| 3 | |||
| 4 | |||
| 5 | |||
| 6 | Support | ||
To install a power supply, complete the following steps.